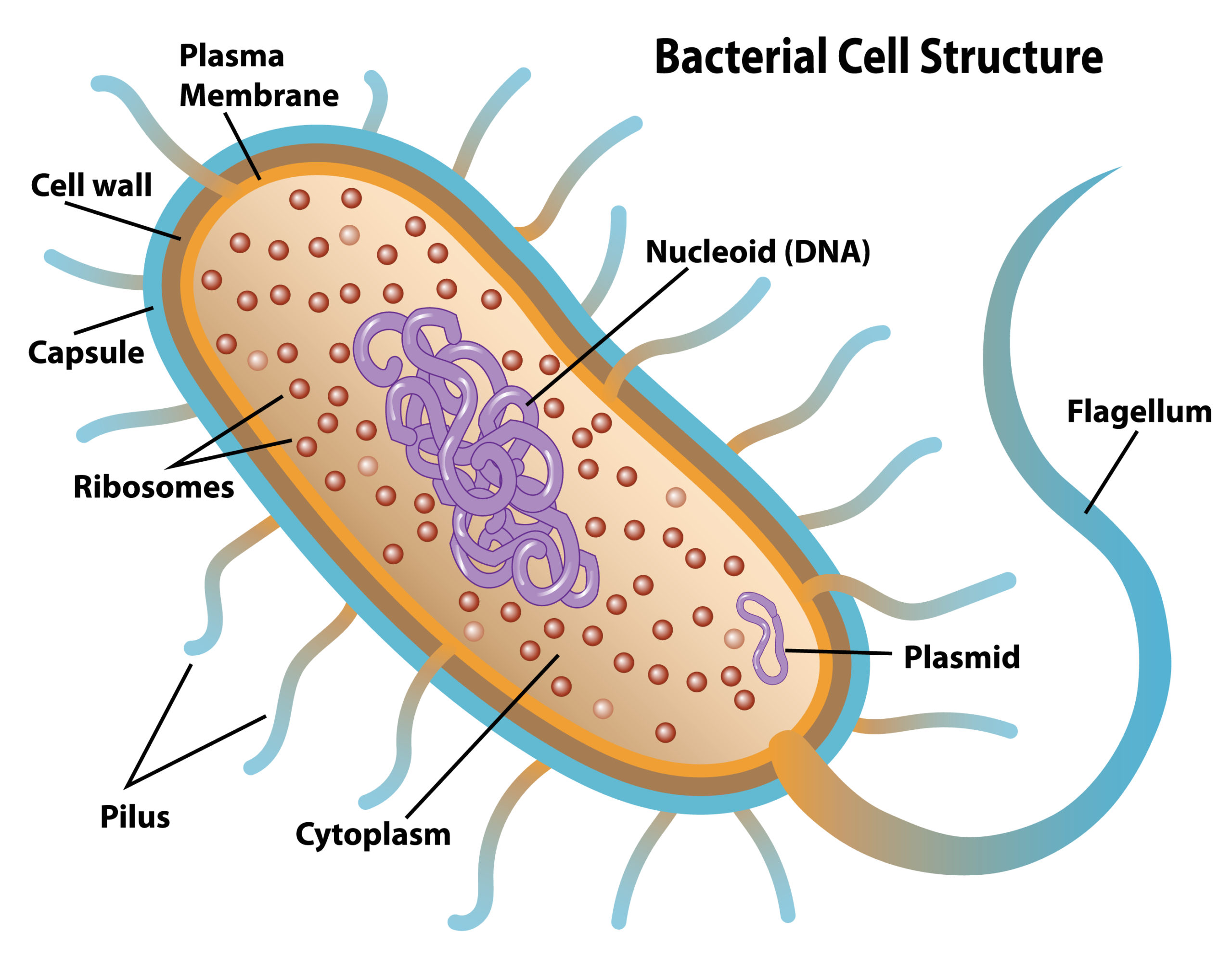
Plasmid
Description Plasmid, in microbiology, an extrachromosomal genetic element that occurs in many bacterial strains. Plasmids are circular deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) molecules that replicate independently of the bacterial chromosome. They are not essential to the bacterium but may confer a selective advantage. One class of plasmids, colicinogenic (or Col) factors, determines the production of proteins called … Read more