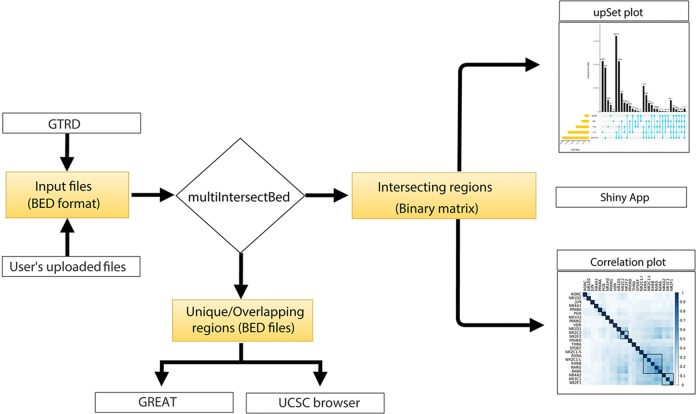
A big quantity of genomic areas, corresponding to transcription issue binding websites (TFBSs) captured from subsequent technology sequencing (NGS) information analyses or these obtainable from the general public useful resource database ENCODE, are usually overlapped to reply a spread of organic questions.
Though a number of command-line instruments can be found to carry out such an evaluation, there’s a notable lack of an built-in webserver software with which to establish genomic area intersections, generate publication-ready plots depicting subsets of the overlapped areas, and carry out purposeful annotation.
Thus, there may be an ardent want for a complete and user-friendly webserver software that enables the customers to both add a number of datasets or choose from the built-in Gene Transcription Regulation Database (GTRD).
Moreover, analyses, together with purposeful annotation, gene ontology, and organic pathways enrichment for the recognized distinctive and intersected genomic areas, may also be carried out utilizing the built-in GREAT instrument.
To view the genomic areas within the genome browser, the inbuilt hyperlink for UCSC can redirect the person to visualize the outcomes as customized tracks.
Informing illness modelling with brain-relevant purposeful genomic annotations.
The previous decade has seen a surge within the quantity of illness/trait-associated variants, largely as a result of of the union of research to share genetic information and the provision of digital well being data from massive cohorts for analysis use.
Variant discovery for neurological and neuropsychiatric genome-wide affiliation research, together with schizophrenia, Parkinson’s illness and Alzheimer’s illness, has drastically benefitted; nonetheless, the interpretation of these genetic affiliation outcomes to interpretable organic mechanisms and fashions is lagging.
Interpreting disease-associated variants requires data of gene regulatory mechanisms and computational instruments that let integration of this information with genome-wide affiliation research outcomes.
Here, we summarize key conceptual advances within the technology of brain-relevant purposeful genomic annotations and amongst instruments that enable integration of these annotations with affiliation abstract statistics, which collectively present a brand new and thrilling alternative to establish disease-relevant genes, pathways and cell varieties in silico.
We talk about the alternatives and challenges related to these developments and conclude with our perspective on future advances in annotation technology, instrument improvement and the union of the 2.
